OLMo
Overview
In this guide, we provide an overview of the Open Language Model (OLMo), including prompts and usage examples. The guide also includes tips, applications, limitations, papers, and additional reading materials related to OLMo.
Introduction to OLMo
The Allen Institute of AI has released a new open language model and framework called OLMo. This effort is meant to provide full access to data, training code, models, and evaluation code to accelerate the study of language models collectively.
Model Variants
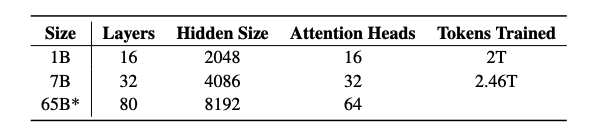
Their first release includes:
- Four variants at the 7B parameter scale
- One model at the 1B scale
- All trained on at least 2T tokens
Future: This marks the first of many releases, including an upcoming 65B OLMo model.
Complete Release Package
The releases include:
- Full training data, including the code that produces the data
- Full model weights, training code, logs, metrics, and inference code
- Several checkpoints per model
- Evaluation code
- Fine-tuning code
Licensing
All the code, weights, and intermediate checkpoints are released under the Apache 2.0 License.
OLMo-7B
Architecture
Both the OLMo-7B and OLMo-1B models adopt a decoder-only transformer architecture with improvements from other models like PaLM and Llama:
- No biases
- Non-parametric layer norm
- SwiGLU activation function
- Rotary positional embeddings (RoPE)
- Vocabulary: 50,280 tokens
Dolma Dataset
Dataset Overview
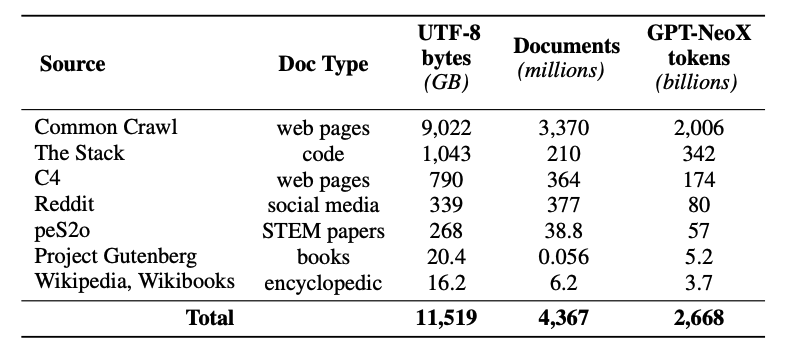
This release also includes a pre-training dataset called Dolma -- a diverse, multi-source corpus of 3 trillion tokens across 5B documents acquired from 7 different data sources.
Data Processing
The creation of Dolma involves several steps:
- Language filtering
- Quality filtering
- Content filtering
- Deduplication
- Multi-source mixing
- Tokenization
Training Details
The training dataset includes a 2T-token sample from Dolma:
- Tokens are concatenated together after appending a special EOS token to the end of each document
- Training instances include groups of consecutive chunks of 2048 tokens
- Chunks are shuffled during training
Note: More training details and hardware specifications can be found in the paper.
Results
Evaluation Framework
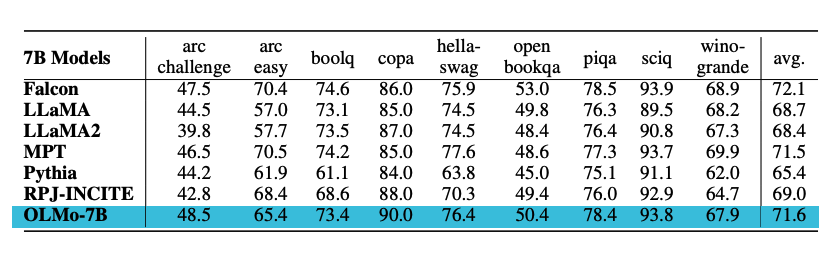
The models are evaluated on downstream tasks using Catwalk. OLMo models are compared to several publicly available models like Falcon and Llama 2.
Evaluation Tasks
The model is evaluated on tasks that measure commonsense reasoning abilities:
- Datasets: piqa and hellaswag
- Method: Zero-shot evaluation using rank classification (completions ranked by likelihood)
- Metric: Accuracy
Performance Summary
OLMo-7B:
- Outperforms all other models on 2 end-tasks
- Remains top-3 on 8/9 end-tasks
Prompting Guide for OLMo
Coming soon...
Figures source: OLMo: Accelerating the Science of Language Models
Key Takeaways
- Full Openness: Complete access to data, code, weights, and checkpoints
- Multiple Scales: 1B, 7B, and upcoming 65B parameter variants
- Advanced Architecture: Decoder-only transformer with modern improvements
- Quality Dataset: 3T token Dolma corpus from diverse sources
- Strong Performance: Top-3 performance on 8/9 commonsense reasoning tasks
- Research Focus: Designed to accelerate language model science
- Apache 2.0 License: Fully open source for research and development
