Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Overview
General-purpose language models can be fine-tuned to achieve several common tasks such as sentiment analysis and named entity recognition. These tasks generally don't require additional background knowledge.
For more complex and knowledge-intensive tasks, it's possible to build a language model-based system that accesses external knowledge sources to complete tasks. This enables more factual consistency, improves reliability of the generated responses, and helps to mitigate the problem of "hallucination".
What is RAG?
Meta AI researchers introduced a method called Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to address such knowledge-intensive tasks. RAG combines an information retrieval component with a text generator model. RAG can be fine-tuned and its internal knowledge can be modified in an efficient manner and without needing retraining of the entire model.
How It Works
RAG takes an input and retrieves a set of relevant/supporting documents given a source (e.g., Wikipedia). The documents are concatenated as context with the original input prompt and fed to the text generator which produces the final output. This makes RAG adaptive for situations where facts could evolve over time. This is very useful as LLMs's parametric knowledge is static. RAG allows language models to bypass retraining, enabling access to the latest information for generating reliable outputs via retrieval-based generation.
Technical Implementation
Lewis et al., (2021) proposed a general-purpose fine-tuning recipe for RAG. A pre-trained seq2seq model is used as the parametric memory and a dense vector index of Wikipedia is used as non-parametric memory (accessed using a neural pre-trained retriever). Below is an overview of how the approach works:
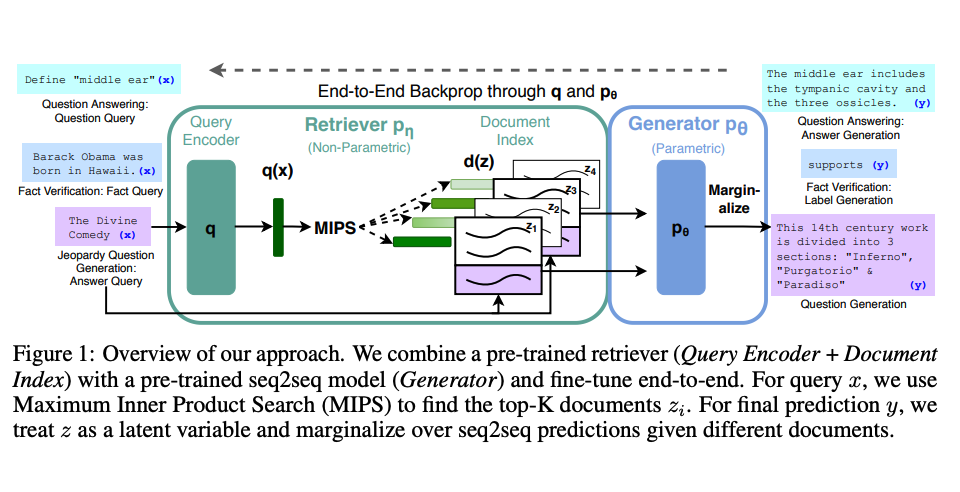
Image Source: Lewis et al. (2021)
Performance Results
RAG performs strong on several benchmarks such as Natural Questions, WebQuestions, and CuratedTrec. RAG generates responses that are more factual, specific, and diverse when tested on MS-MARCO and Jeopardy questions. RAG also improves results on FEVER fact verification.
This shows the potential of RAG as a viable option for enhancing outputs of language models in knowledge-intensive tasks.
Recent Developments
More recently, these retriever-based approaches have become more popular and are combined with popular LLMs like ChatGPT to improve capabilities and factual consistency.
Use Case: Generating Friendly ML Paper Titles
Below, we have prepared a notebook tutorial showcasing the use of open-source LLMs to build a RAG system for generating short and concise machine learning paper titles:
Getting Started with RAG
The tutorial demonstrates how to:
- Set up a document retrieval system
- Integrate with language models
- Generate context-aware responses
- Improve factual accuracy
Key Benefits
- Factual Consistency: Reduces hallucination through external knowledge
- Up-to-date Information: Access to current information without retraining
- Efficient Knowledge Integration: Combines parametric and non-parametric memory
- Scalable Architecture: Works with various knowledge sources and models
- Improved Reliability: More accurate and trustworthy responses
Applications
- Question Answering: Complex queries requiring external knowledge
- Document Summarization: Creating summaries with factual verification
- Research Assistance: Supporting academic and professional research
- Content Generation: Creating accurate, up-to-date content
- Fact Checking: Verifying claims against reliable sources
Related Topics
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting - Understanding reasoning techniques
- Few-Shot Prompting - Learning from examples
- Prompt Engineering Guide - General prompt engineering techniques
References
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey (Dec 2023)
- Retrieval Augmented Generation: Streamlining the creation of intelligent natural language processing models (Sep 2020)
- Lewis et al., (2021) - Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks
