Multimodal CoT Prompting
Overview
Zhang et al. (2023) recently proposed a multimodal chain-of-thought prompting approach. Traditional CoT focuses on the language modality. In contrast, Multimodal CoT incorporates text and vision into a two-stage framework. The first step involves rationale generation based on multimodal information. This is followed by the second phase, answer inference, which leverages the informative generated rationales.
Key Innovation
The multimodal CoT model (1B) outperforms GPT-3.5 on the ScienceQA benchmark.
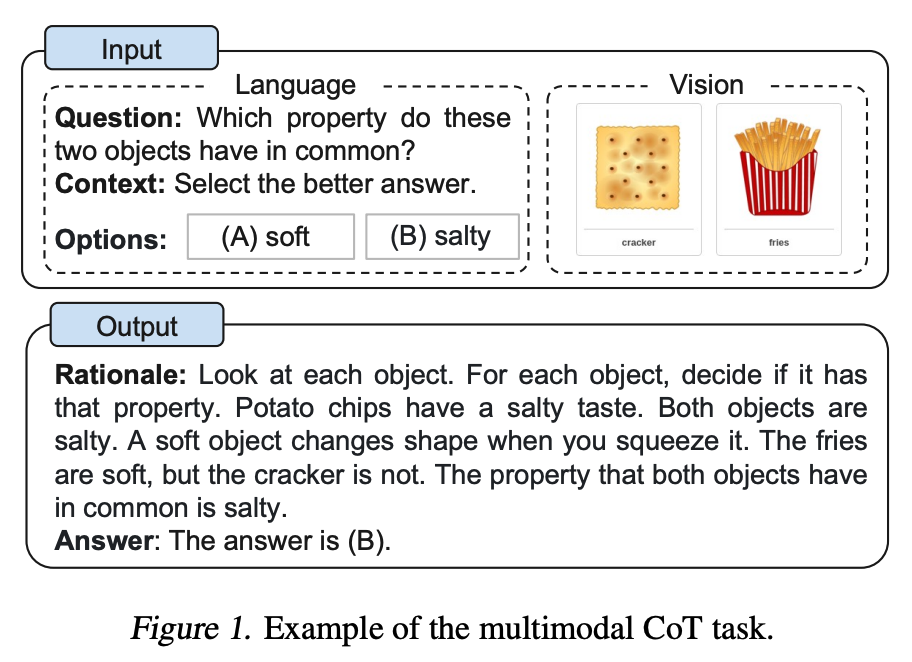
Image Source: Zhang et al. (2023)
How It Works
Multimodal CoT extends traditional chain-of-thought prompting by:
- Multimodal Input Processing: Combines text and visual information
- Two-Stage Framework:
- Stage 1: Generate reasoning based on multimodal context
- Stage 2: Infer answers using the generated rationales
- Enhanced Reasoning: Leverages visual cues for better understanding
Applications
- Visual Question Answering: Answering questions about images
- Science Education: Explaining scientific concepts with diagrams
- Document Analysis: Understanding documents with visual elements
- Multimodal Reasoning: Tasks requiring both text and visual understanding
Key Benefits
- Multimodal Understanding: Processes both text and visual information
- Enhanced Reasoning: Better reasoning through visual context
- Improved Performance: Outperforms text-only models on visual tasks
- Educational Applications: Effective for explaining visual concepts
Related Topics
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting - Understanding CoT prompting techniques
- Few-Shot Prompting - Learning from examples
- Prompt Engineering Guide - General prompt engineering techniques
Further Reading
References
- Zhang et al. (2023) - Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Language Models
