Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models
Overview
This paper explores the benefits of scaling instruction finetuning and how it improves performance on a variety of models (PaLM, T5), prompting setups (zero-shot, few-shot, CoT), and benchmarks (MMLU, TyDiQA). This is explored with the following aspects: scaling the number of tasks (1.8K tasks), scaling model size, and finetuning on chain-of-thought data (9 datasets used).
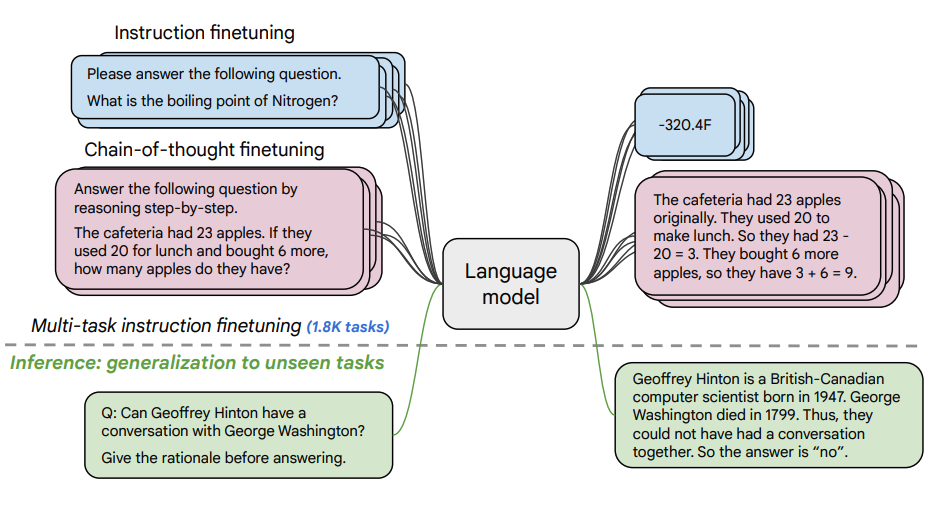
Finetuning Procedure
Task Scaling
- 1.8K tasks were phrased as instructions and used to finetune the model
- Uses both with and without exemplars, and with and without CoT
- Finetuning tasks and held out tasks shown below:
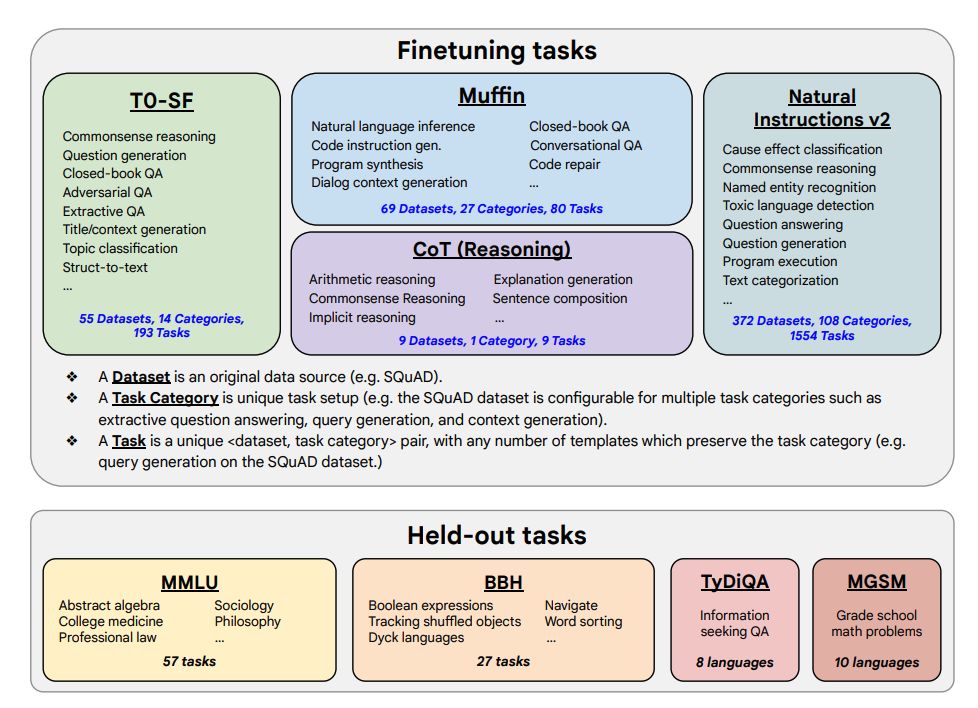
Capabilities & Key Results
Performance Improvements
- Instruction finetuning scales well with the number of tasks and the size of the model
- This suggests the need for scaling number of tasks and size of model further
- Adding CoT datasets into the finetuning enables good performance on reasoning tasks
Multilingual Capabilities
- Flan-PaLM has improved multilingual abilities
- 14.9% improvement on one-shot TyDiQA
- 8.1% improvement on arithmetic reasoning in under-represented languages
Generation Quality
- Plan-PaLM performs well on open-ended generation questions
- This is a good indicator for improved usability
- Improves performance across responsible AI (RAI) benchmarks
Model Comparison
- Flan-T5 instruction tuned models demonstrate strong few-shot capabilities
- Outperforms public checkpoints such as T5
Scaling Analysis
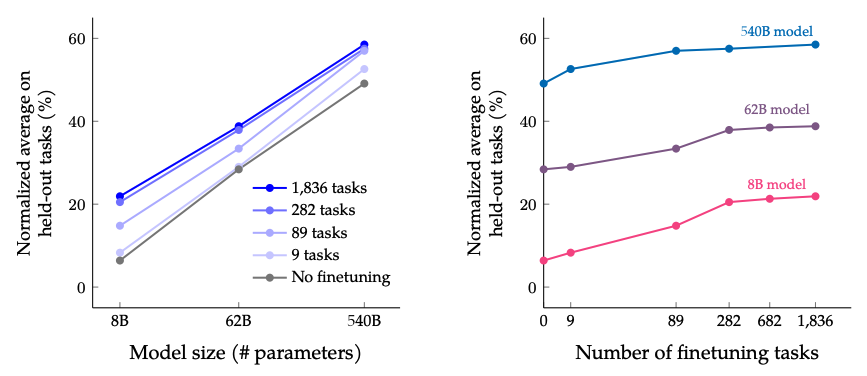
Task and Model Size Scaling
The results when scaling number of finetuning tasks and model size: scaling both the size of the model and the number of finetuning tasks is expected to continue improving performance, although scaling the number of tasks has diminished returns.
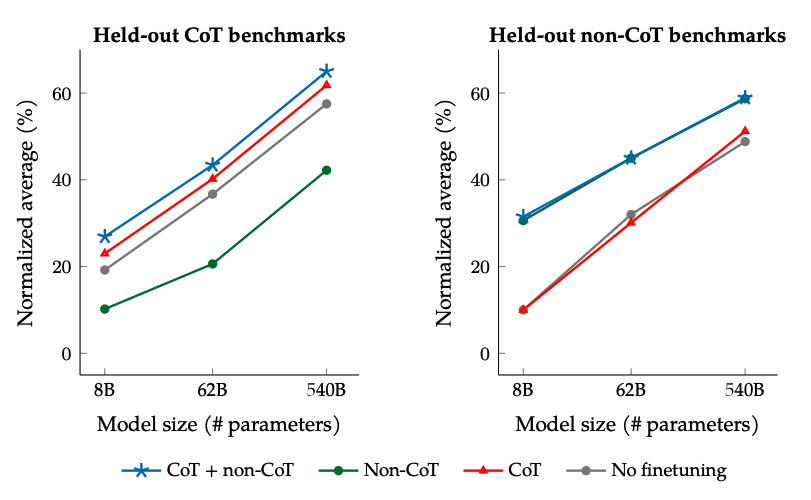
CoT vs Non-CoT Finetuning
The results when finetuning with non-CoT and CoT data: Jointly finetuning on non-CoT and CoT data improves performance on both evaluations, compared to finetuning on just one or the other.
Self-Consistency with CoT
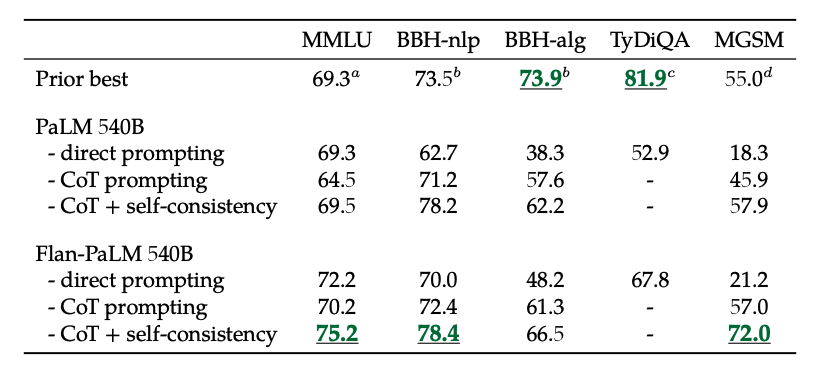
In addition, self-consistency combined with CoT achieves SoTA results on several benchmarks. CoT + self-consistency also significantly improves results on benchmarks involving math problems (e.g., MGSM, GSM8K).
Zero-Shot Chain-of-Thought
Activation and Performance
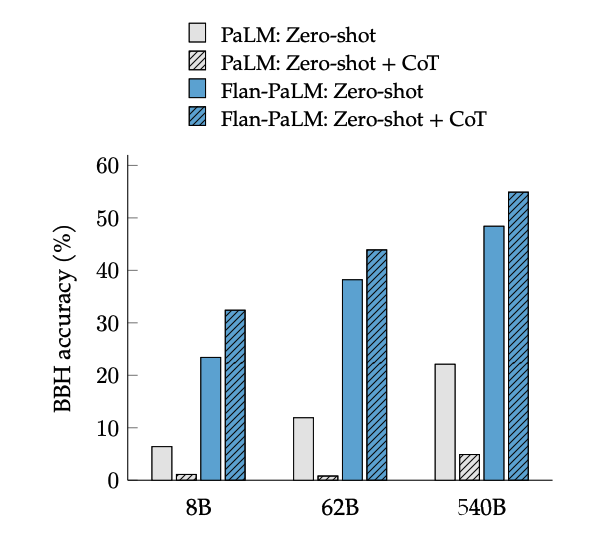
CoT finetuning unlocks zero-shot reasoning, activated by the phrase "let's think step-by-step", on BIG-Bench tasks. In general, zero-shot CoT Flan-PaLM outperforms zero-shot CoT PaLM without finetuning.
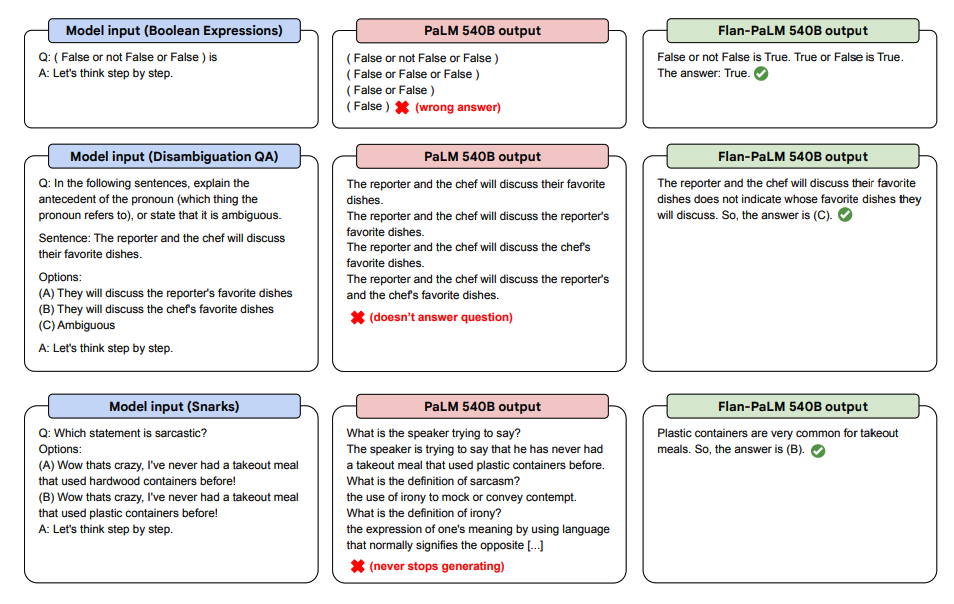
Zero-Shot Demonstrations
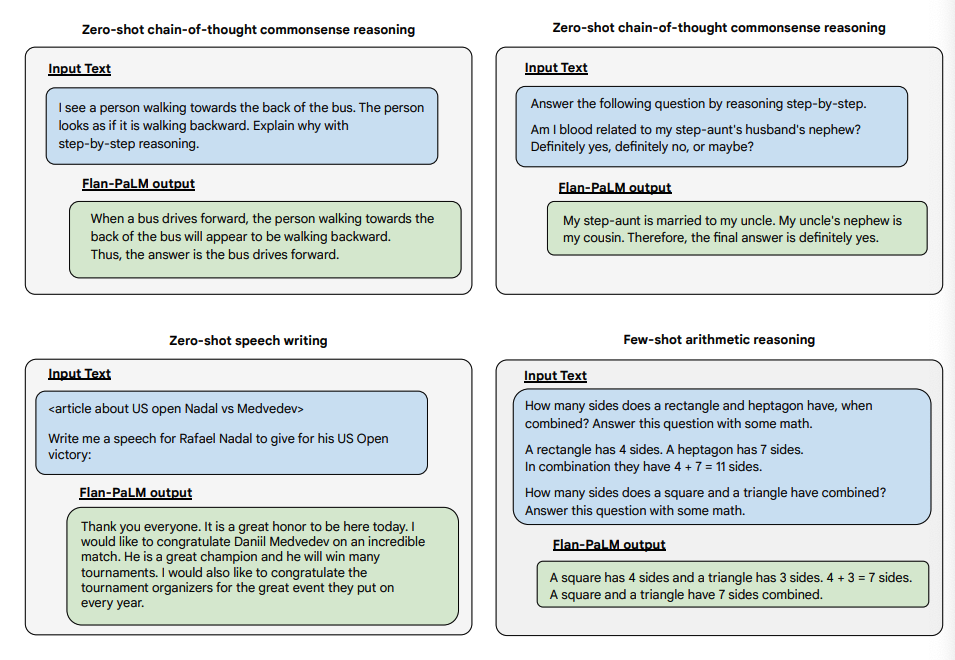
Below are some demonstrations of zero-shot CoT for PaLM and Flan-PaLM in unseen tasks.
Additional Zero-Shot Capabilities
Below are more examples for zero-shot prompting. It shows how the PaLM model struggles with repetitions and not replying to instructions in the zero-shot setting where the Flan-PaLM is able to perform well. Few-shot exemplars can mitigate these errors.

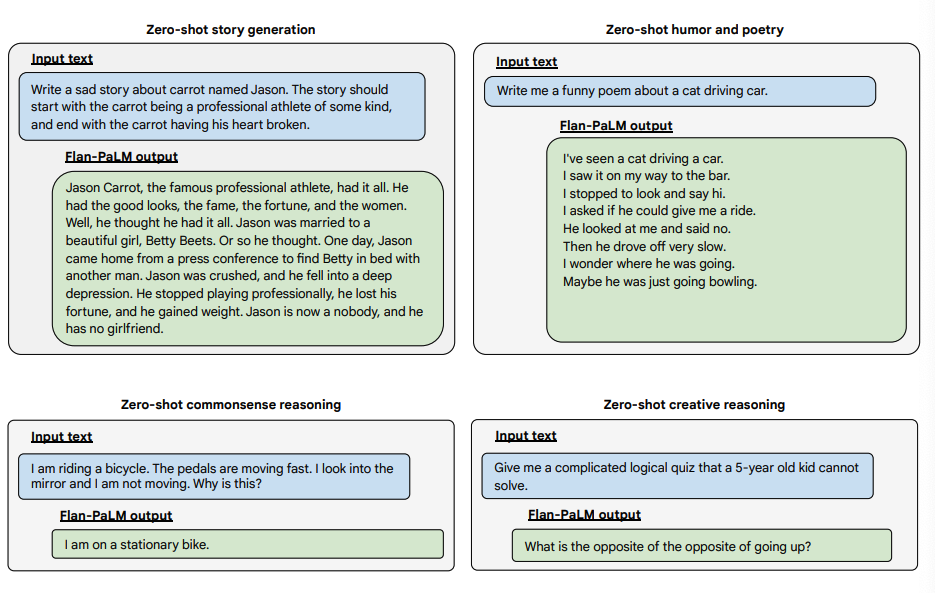
Open-Ended Question Examples
Below are some examples demonstrating more zero-shot capabilities of the Flan-PALM model on several different types of challenging open-ended questions:
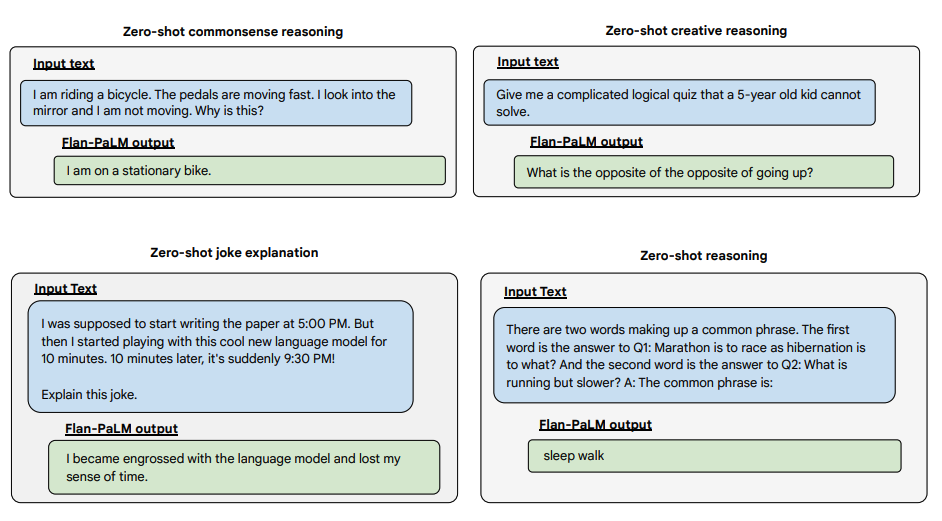
Try It Out
You can try Flan-T5 models on the Hugging Face Hub.
Key Takeaways
- Instruction finetuning scales effectively with both task count and model size
- CoT integration significantly improves reasoning capabilities
- Multilingual performance shows substantial improvements
- Zero-shot reasoning is unlocked through proper finetuning
- Self-consistency combined with CoT achieves state-of-the-art results
- Open-ended generation quality is significantly improved
