Automatic Reasoning and Tool-use (ART)
Overview
Combining CoT prompting and tools in an interleaved manner has shown to be a strong and robust approach to address many tasks with LLMs. These approaches typically require hand-crafting task-specific demonstrations and carefully scripted interleaving of model generations with tool use. Paranjape et al., (2023) propose a new framework that uses a frozen LLM to automatically generate intermediate reasoning steps as a program.
How It Works
ART works as follows:
- Demonstration Selection: Given a new task, it selects demonstrations of multi-step reasoning and tool use from a task library
- Tool Integration: At test time, it pauses generation whenever external tools are called, and integrates their output before resuming generation
- Generalization: ART encourages the model to generalize from demonstrations to decompose a new task and use tools in appropriate places, in a zero-shot fashion
In addition, ART is extensible as it also enables humans to fix mistakes in the reasoning steps or add new tools by simply updating the task and tool libraries. The process is demonstrated below:
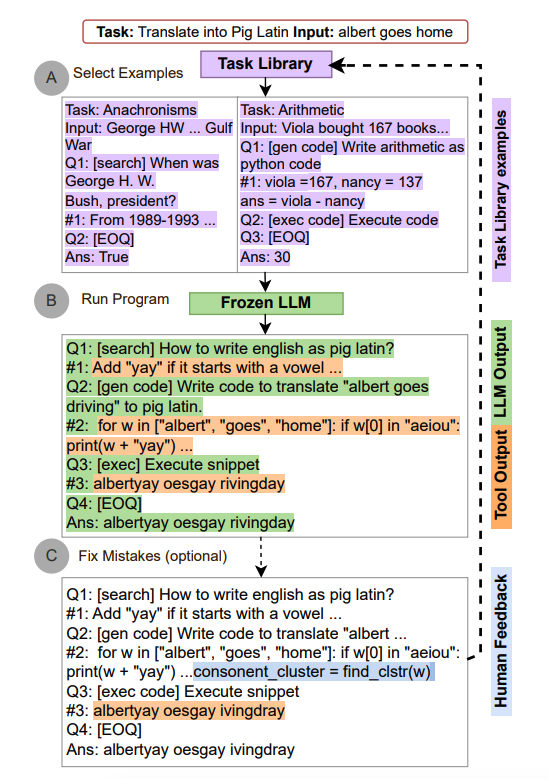
Image Source: Paranjape et al., (2023)
Performance Results
ART substantially improves over few-shot prompting and automatic CoT on unseen tasks in the BigBench and MMLU benchmarks, and exceeds performance of hand-crafted CoT prompts when human feedback is incorporated.
Below is a table demonstrating ART's performance on BigBench and MMLU tasks:
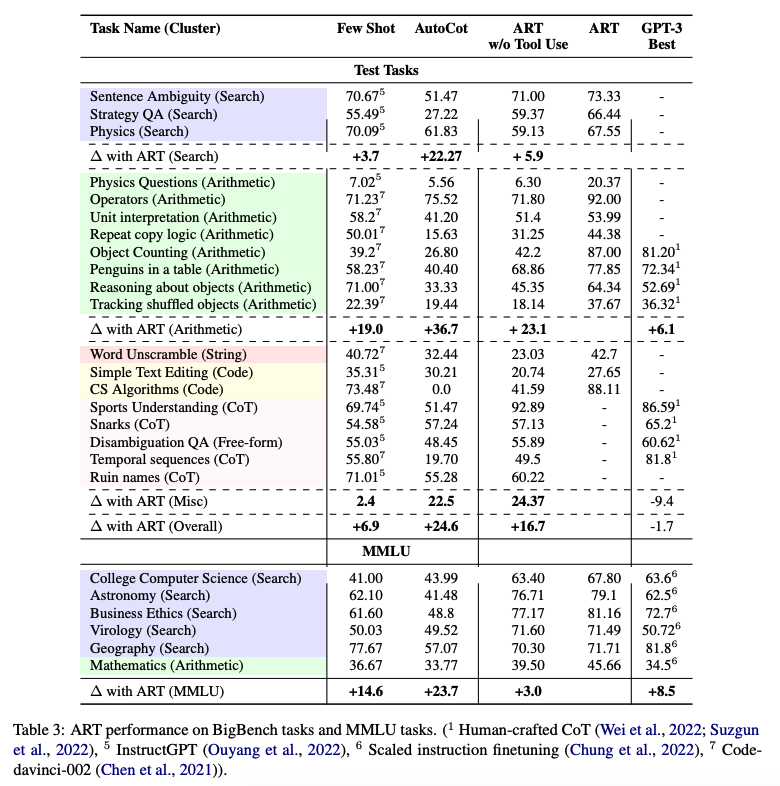
Image Source: Paranjape et al., (2023)
Key Benefits
- Zero-Shot Generalization: Works on unseen tasks without retraining
- Automatic Reasoning: Generates intermediate reasoning steps automatically
- Tool Integration: Seamlessly integrates external tools and APIs
- Human Oversight: Allows human intervention and correction
- Extensible Framework: Easy to add new tools and tasks
Applications
- Complex reasoning tasks requiring external information
- Multi-step problem solving
- Tool-augmented language models
- Automated reasoning systems
- Task decomposition and planning
Related Topics
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting - Understanding CoT prompting techniques
- ReAct Prompting - Combining reasoning and acting
- Prompt Engineering Guide - General prompt engineering techniques
References
- Paranjape et al., (2023) - ART: Automatic Reasoning and Tool-use
